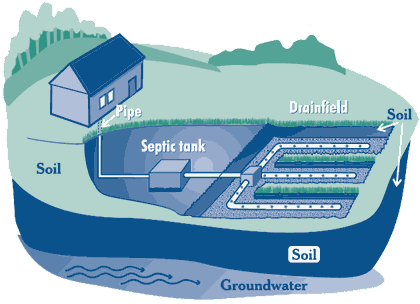
A septic tank, the key
component of a septic system, is a small scale sewage
treatment system common in areas with no connection to main
sewage pipes provided by private corporations or local
governments. (Other components, typically mandated and/or
restricted by local governments, optionally include pumps,
alarms,
sand filters, and clarified liquid effluent disposal
means such as a septic drain field. Septic systems are
a type of On-Site Sewage Facility.
In North America approximately
25% of the population relies on septic tanks; this can
include suburbs and small towns as well as rural areas.
Indianapolis, Indiana is an example of a large city where
much of the city's neighborhoods are still on separate
septic systems. In Europe they are generally limited
to rural areas only.
The term "septic" refers to the
anaerobic bacterial environment that develops in the tank
and which decomposes or mineralizes the waste discharged
into the tank. Adding a supplemental bacterial agent
(enzymes) to the tank may accelerate the digestion of
solids in the tank. Septic tanks can be coupled with other
on-site wastewater treatment units such as biofilters or
aerobic systems involving artificial forced aeration.
Periodic preventive
maintenance is required to remove the irreducible solids
which settle and gradually fill the tank, reducing its
efficiency. In most jurisdictions this maintenance is
required by law, yet often not enforced. Those who
ignore the requirement will eventually be faced with
extremely costly repairs when solids escape the tank and
destroy the clarified liquid effluent disposal means. A
properly cared-for system, on the other hand, can last
for decades and possibly a lifetime.
 Prevent
Costly Repairs To Septic Systems By Maintaining Proper
Enzyme Levels:
Prevent
Costly Repairs To Septic Systems By Maintaining Proper
Enzyme Levels:
It is recommended to use an
enzyme additive to keep the septic system working properly.
Enzyme additives helps prevent septic drain field failure,
costly repairs and possible excavation of the septic field.
Dissolves Grease, Fats, Paper, Starches and Protein.
Concentrated, 100% natural Bio-enzymatic active ingredients.
Where To Buy Drain Out Enzyme Septic System Treatment
 Keep
Roots From Growing Into Your Septic Field Or Pipes:
Keep
Roots From Growing Into Your Septic Field Or Pipes:
Roots of shrubbery and trees growing near sewer lines frequently penetrate
pipes in search of moisture and nutrients. If not controlled, root hairs will
grow in diameter and number causing tile breakage, gradual reduced flow, and
sometimes complete stoppage. Root Clear is effective in keeping sewer lines free
of harmful roots. It is safe for drain systems and does not harm outdoor
shrubbery or trees.
Where To Buy Root Clear For Sewers, Drains And Septic Systems

Potential septic tank problems:
- Excessive dumping of cooking oils and grease can fill up the upper portion of the septic tank and can
cause the inlet drains to block. Oils and grease are often difficult to degrade and can cause odor
problems and difficulties with the periodic emptying.
- Flushing non-biodegradable hygiene products such as sanitary towels
and cotton balls will rapidly fill or clog a septic tank; these materials
should not be disposed of in this way.
Use Drain Out Enzyme Septic System Treatment to help prevent this
problem.
- The use of garbage disposals for waste food can cause a
rapid overload of the system and early failure.
- Certain chemicals may damage the operation of a septic tank,
especially pesticides, herbicides, materials with high concentrations of
bleach or caustic soda (lye) or any other inorganic materials such as
paints or solvents.
- Roots from trees and shrubbery growing above the tank or the drain
field may clog and or rupture them. Use
Root Clear to prevent this problem.
- Playgrounds and storage buildings may cause damage to a tank and the
drainage field. In addition, covering the drainage field with an
impervious surface, such as a driveway or parking area, will seriously
affect its efficiency and possibly damage the tank and absorption
system.
- Excessive water entering the system will overload it and cause it to
fail. Checking for plumbing leaks and practicing water conservation will
help the system's long term operation.
- Even well maintained septic tanks release
mucus-producing
anaerobic gut bacteria to the drainage field. The mucus "slime" will
slowly clog the soil pores surrounding the drain pipe and percolation
can slow to the point where backups or surfacing effluent can occur.
This slime is called Biomat and such a failure is referred to as "Biomat
failure".
- If the system is damaged or malfunctions, contact your local health
or environmental authority before attempting any repairs. Improper
repair can result in costly mistakes and potential health hazards.
- Septic tanks by themselves are ineffective at removing
nitrogen compounds that can cause
algae blooms in receiving waters; this can be remedied by using a
nitrogen-reducing technology.